Restore. Rebalance. Revive.
Lifestyle Medicine I Medical Acupuncture
Searching for more than just a quick fix?
What if true healing goes deeper than just the symptoms?
DIVING DEEPER, RISING STRONGER
We believe in a deeply personalized, integrative approach to health. Our philosophy intertwines the ancient wisdom of medical acupuncture with the evidenced-based approach of lifestyle medicine and insights of functional medicine, crafting a sanctuary for healing that attends not just to symptoms, but to the root causes
of health challenges.
ROOT TO RISE
Specializing in women's hormonal health, fertility, and mental well-being, we guide our patients through their unique journey towards optimal health. We delve into the intricacies of your unique physiology, lifestyle, and aspirations to curate a wellness plan that resonates with your individual needs. We firmly believe that health is a partnership. We recognize and celebrate your agency in this journey, understanding that true healing and wellness flourish through mutual respect, shared knowledge, and the empowerment of your own choices and actions in pursuit of health.
Medical Acupuncture
• After a thorough initial health evaluation, we offer a personalized treatment strategy and care plan.
$250 initial consult and treatment (75 minutes)$150 follow up treatments (60 minutes)
Lifestyle Medicine
• A comprehensive evaluation of lifestyle habits to provide personalized evidence-based guidance on how to make positive changes. May include recommended testing and supplement plan if needed.
$500 Comprehensive health initial evaluation (75 minutes)$200 Follow up appointments (30 minutes)$150 Each functional test interpretation
Holistic Fertility
• A comprehensive fertility support program for couples who are planning to conceive or trying to conceive.
• Encompasses a functional medicine and naturopathic medicine approach to fertility.
• Tailored to your particular needs with selected appropriate testing (hormonal, adrenal, GI, nutritional, etc.) and therapeutic strategies.
• Embraces the full spectrum of the body including physical health as well as mental, emotional, and spiritual well-being.
• If you have been told you have unexplained infertility, or are confused about the next steps (what diet to follow, what supplements to take, what you can do to optimize your reproductive health, etc.), we can support you.
Facial Rejuvenation
A series of acupuncture treatments combined with lifestyle practices to tone muscles, stimulate blood flow, and increase collagen. A gentle, effective, and safe way to combat the signs of aging, returning the face to a healthier, revitalized, more youthful appearance.
**Combined with LED phototherapy.
Gold Package: 6 treatments $1350Platinum Package: 12 treatments $2350
Microneedling
Collagen induction therapy using a medical grade pen device to improve skin texture, and decrease the appearance of fine lines and acne scarring. Includes LED phototherapy.
$400 single. Package of 4 treatments $1500**Option for
AnteAGE MD Growth Factor ($475 single. Package of 4 treatments $1800)
Acupuncture in Pregnancy
Acupuncture offers a safe, natural, and effective approach to supporting women throughout their pregnancy journey. From promoting relaxation to alleviating common pregnancy-related ailments such as nausea, fatigue, and lower back pain, acupuncture is a holistic tool to enhance maternal wellness.
Dr. Audrey Le has extensive experience in providing acupuncture during pregnancy, helping women experience a smoother, more comfortable pregnancy while supporting both maternal and fetal health. She utilizes evidence-based acupuncture techniques to promote the body’s natural healing processes, ensuring safe and effective treatment throughout the pregnancy stages.
Benefits of Acupuncture in Pregnancy:
Morning Sickness Relief: Acupuncture can help reduce nausea and vomiting associated with pregnancy, offering natural relief without the need for medications.
Managing Pain:
Pregnancy-related back pain, pelvic discomfort, and sciatica can be eased through acupuncture, promoting greater comfort.
Improved Sleep:
Acupuncture can help address sleep disturbances, which are common in pregnancy, allowing women to rest better.
Boosting Energy:
Pregnancy often brings fatigue and exhaustion; acupuncture can help restore energy and Full Width balance.
Support during Labor:
Acupuncture can be used to prepare the body for labor, helping to manage pain and reduce anxiety during delivery.
Dr. Le carefully customizes each treatment to meet the unique needs of the individual, always prioritizing both the safety of the mother and the health of the baby.
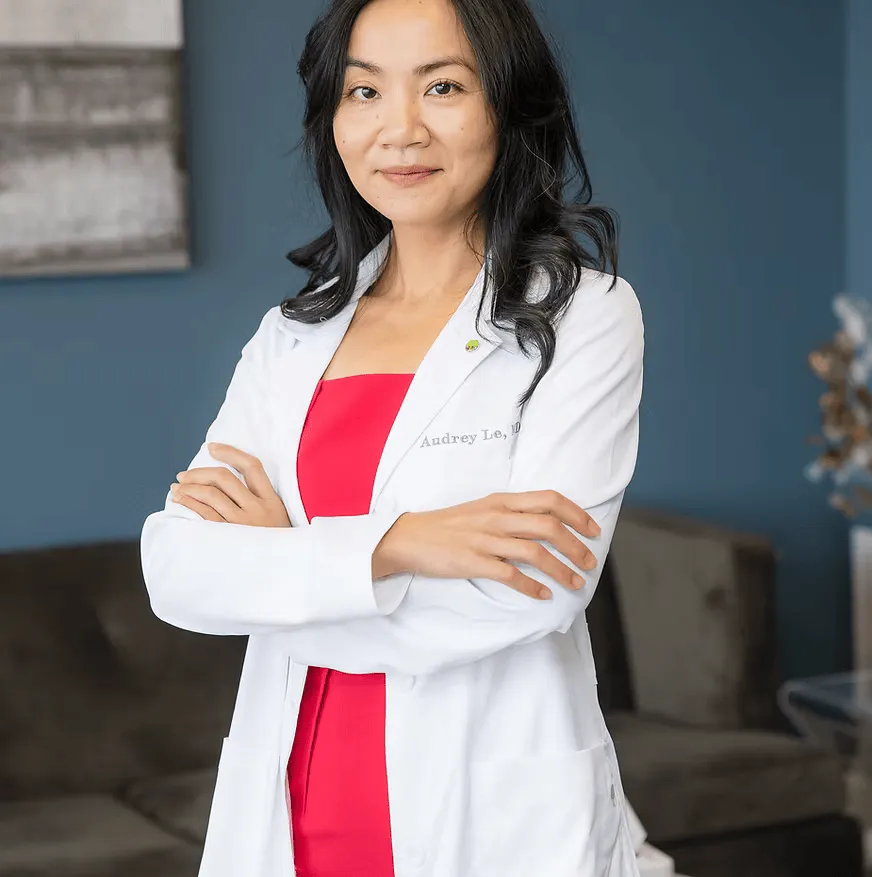

Meet Audrey Le, MD
Dr. Audrey Le brings over two decades of medical experience to her holistic practice, blending traditional and modern healing techniques to offer comprehensive care. A graduate of the University of Mississippi Medical Center, Dr. Le has deepened her expertise by training with the Holistic Fertility Institute, focusing on integrating holistic approaches into fertility, women's health, and mental wellness.
Recognizing the profound benefits of acupuncture, Dr. Le pursued and received certifications in medical acupuncture and dry needling, placing her among the select few physician acupuncturists licensed in Louisiana. Her passion for medical acupuncture drives her practice; she combines ancient techniques with contemporary medical insights to provide a holistic, scientifically-backed approach to patient care.
Her professional affiliations include the American Academy of Medical Acupuncture, the American College of Lifestyle Medicine , the
Institute for Functional Medicine , and she is a Senior Member of the Obstetric Acupuncture Association (OBAA). Additionally, Dr. Le has completed a year-long herbal fellowship with the American Association for the Advancement of Restorative Medicine , further enhancing her ability to provide tailored, effective treatments to her patients.
Contact Info
Office Hours: Mon/Tues/Thurs: 8:30am - 4:00pm
Fri: 8:30 am - 12:00 pm
Copyrights 2024 | Audrey Le MD™ | Terms & Conditions